Uni codes breast cancer bots
 Australian researchers are training AI to spot breast cancer.
Australian researchers are training AI to spot breast cancer.
Researchers from the University of Adelaide’s Australian Institute for Machine Learning (AIML) are developing a fully-automated medical image analysis program to detect breast tumours.
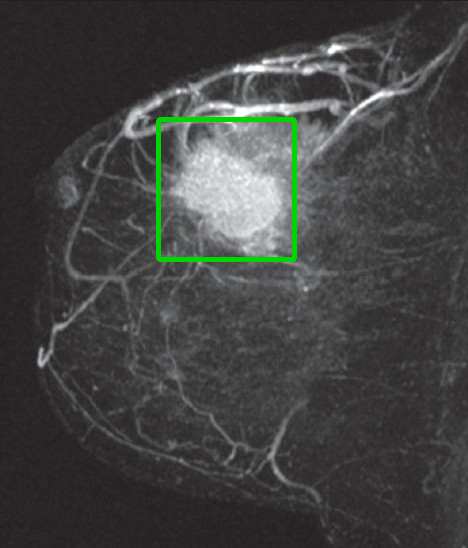
In conjunction with an MRI scan, the AI system looks like a top-down view of the retro video game Tetris.
“Just as vintage video game Tetris manipulated geometric shapes to fit a space, this program uses a green square to navigate and search over the breast image to locate lesions. The square changes to red in colour if a lesion is detected,” says Mr University of Adelaide PhD candidate Gabriel Maicas Suso.
“Our research shows that this unique approach is 1.78 times faster in finding a lesion than existing methods of detecting breast cancer, and the results are just as accurate.”
The program was designed using deep reinforcement learning methods, a form of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers and machines to learn how to do complex tasks without being programmed by humans. As a result, the program can independently analyse breast tissue.
They were able to train the computer program with a relatively small amount of data, which is a critical challenge in medical imaging.
“By incorporating machine learning into medical imaging analysis, we have developed a program that intuitively locates lesions quickly and accurately,” says Associate Professor Carneiro.
“More research is needed before the program could be used clinically. Our ultimate aim is for this detection method to be used by radiologists to complement, support and assist their important work in making a precise and quick prognosis.
“Artificial intelligence has an important role to play in the imaging medical field, the potential to use AI in this field is boundless,” he says.







 Print
Print